2 READ-TIME
Can harvest help determine future insect pressure in corn?
February 2, 2021
Is there feeding down the ear or do corn ears have rotten tips?
Late-season damage from corn earworm (Figure 1), fall armyworm, western bean cutworm, and European corn borer can damage corn ears and lead to increased incidence of disease and rot.1 Traited corn products with above ground protection from damage by these insects are available.
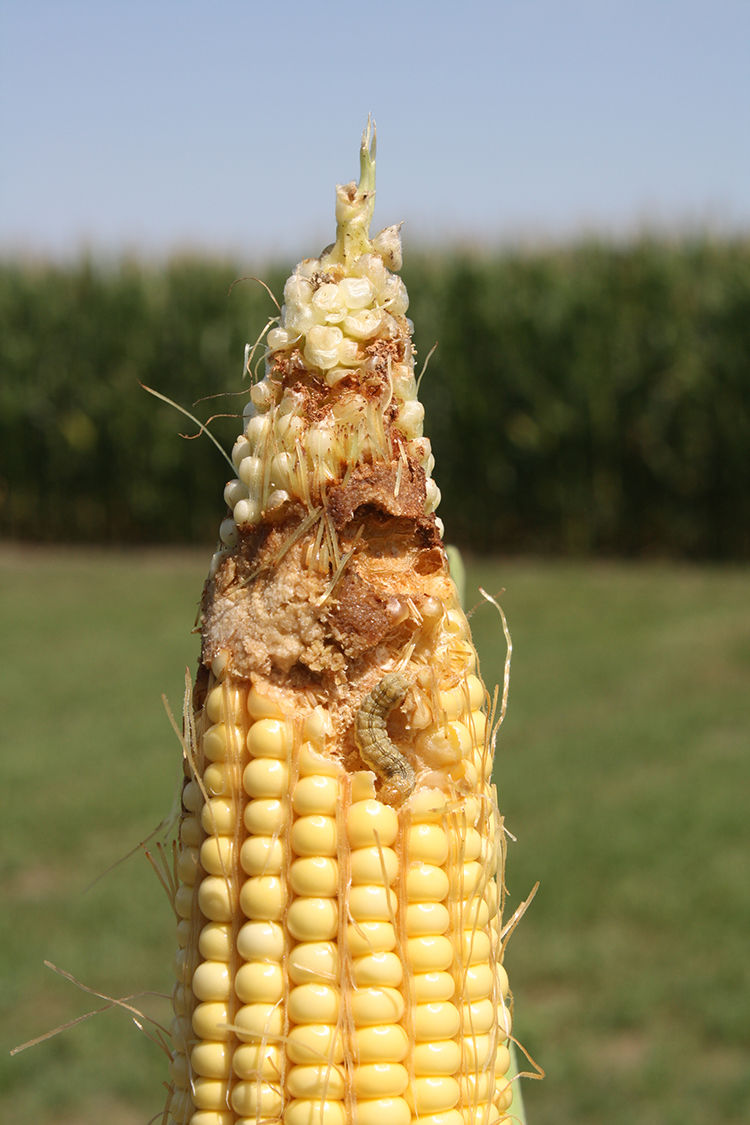

Figure 1. Corn earworm damage to ear.
Was pollination incomplete?
Insects feeding on silks during pollination can cause incomplete pollination. This occurs when silks are clipped to less than 1.3 cm (½-inch) long prior to pollination. Although the insects that caused clipping prior to pollination are no longer a threat to this year’s crop, corn should be scouted for grasshoppers, corn rootworm beetles, corn earworm, and Japanese beetles the following year, as these insects can feed on silks.2
Are random kernels damaged or are ears banana-shaped?
This kind of damage could indicate the presence of stink bugs. Kernels may have scars or appear bruised and dark. Kernels may be mottled in appearance, especially close to the tip of the ear. Heavy stink bug pressure early in the season can lead to deformed, banana-shaped ears. Damage may be caused by brown marmorated, brown, or green stink bugs. 3 The following crop should be closely scouted for stink bug damage and managed accordingly, especially if the field has a history of damage.
Is the crop affected by stalk or root lodging?
Lodged corn has damaged or broken stalks below the ear and can cause substantial harvest delays and losses. Stalk lodging can occur after heavy rain and wind events, or from insect or disease damage. European corn borer larvae tunnel into the stalk or ear shank leading to broken stalks and dropped ears. Damaged stalks are susceptible to stalk rot pathogens, which can lead to stalk lodging. European corn borer and corn rootworm (CRW) damage can increase the incidence of stalk rot. CRW larval feeding can also cause root lodging in corn (Figure 2). Use of traited corn products with above ground protection from European corn borer should be considered in subsequent years.2 The best option for controlling CRW is to rotate out of corn for a minimum of one year. Volunteer corn should be controlled in the rotational crop to ensure CRW does not survive. Pyramided Bt corn products may be used as part of an integrated pest management plan in accordance with Ontario Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs and the Canadian Corn Pest Coalition’s Long-term Responsible Use of Bt Hybrids for Rootworm Management.4
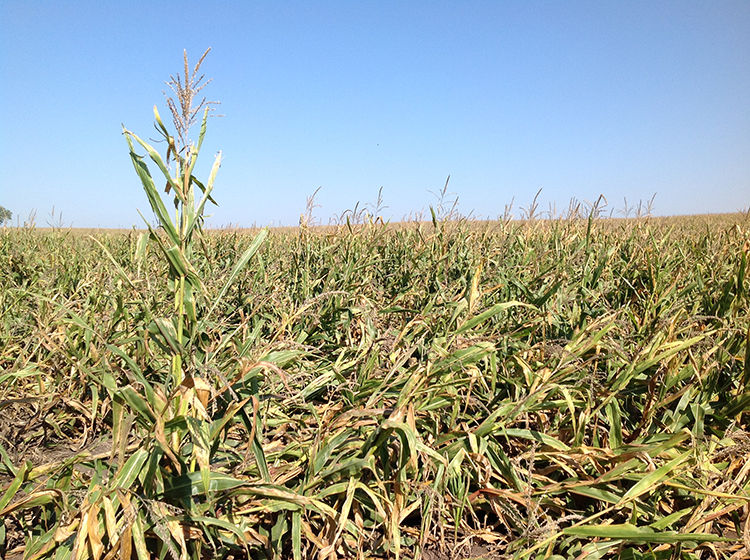

Figure 2. Lodging as a result of corn rootworm feeding.
Sources
1 O’Day, M., Becker, A., Keaster, A., Kabrick, L., and Steffey, K. 1998. Corn insect pests – A diagnostic guide. University of Missouri Extension. https://www.umsystem.edu/.
2 Nielsen, B. and Colville, D. 1988. Stalk lodging in corn: Guidelines for preventive management. Purdue University. AY-262. https://www.extension.purdue.edu/extmedia/AY/AY-262.html
3 Stink bug kernel injury. 2019. The Ohio State University. https://u.osu.edu/mastercorn/stink-bug-kernel-injury/.
4Ontario Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs and Canadian Corn Pest Coalition. 2020. Long-term responsible use of Bt hybrids for corn rootworm management. https://fieldcropnews.com/2020/10/mitigation-measures-for-bt-resistant-corn-rootworm/
Web sources verified -1/23/21
Legal Statements
Performance may vary from location to location and from year to year, as local growing, soil and weather conditions may vary. Growers should evaluate data from multiple locations and years whenever possible and should consider the impacts of these conditions on the grower’s fields.
©2021 Bayer Group. All rights reserved. 7004_Q1_CA